The price of objects resembling sugar and cabbage, which got here below stress as individuals rushed to replenish on provides, declined on a weekly foundation.

Russian weekly inflation slowed to a degree final seen earlier than the invasion of Ukraine in February, a turnaround helped by a stronger ruble and the tip of panic shopping for that brought on some snap shortages.
Value development was simply 0.2% within the seven days ended April 15, slowing for the sixth week in a row and now at lower than a tenth the tempo in early March, the Federal Statistics Service mentioned Wednesday.
The price of objects resembling sugar and cabbage, which got here below stress as individuals rushed to replenish on provides, declined on a weekly foundation. Even costs of durables like home vehicles and vacuum cleaners fell barely.
The reprieve has already allowed the central financial institution to unwind a part of its emergency enhance in rates of interest and promise extra financial easing to come back. Nonetheless, Financial institution of Russia Governor Elvira Nabiullina has warned the economic system faces a reckoning as worldwide sanctions imposed over the warfare in Ukraine power enterprise to regulate by depriving them of many imported parts and disrupting provide chains.
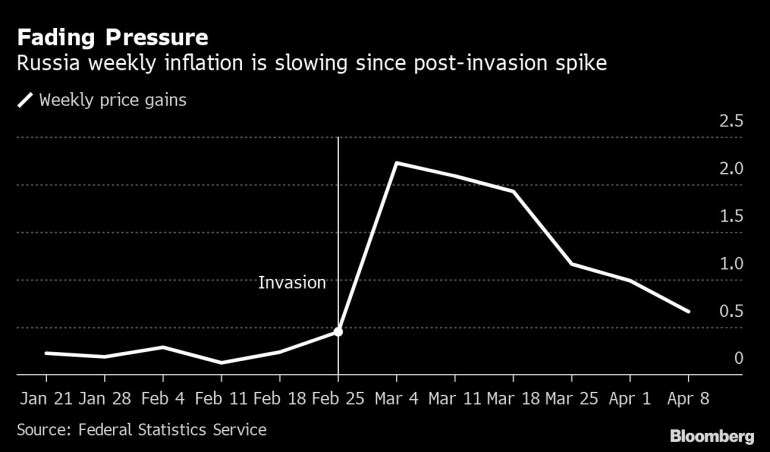
Client demand has already buckled amid fears of further sanctions, and annual inflation is approaching 20%. Development in factory-gate costs, an early indicator of inflation, accelerated additional in March and reached almost 27% from a 12 months earlier, in line with the statistics service.
The Financial institution of Russia has responded by easing a few of its capital controls and chopping its key price to 17% from 20% as focus shifts to supporting the economic system. Measures imposed to calm markets after the assault on Ukraine additionally helped put a brake on client costs by reversing declines within the ruble.
The economic system is dealing with a deep, two-year recession, with this a contraction in gross home product forecast at 8.5% in 2022 by the Worldwide Financial Fund. Nabiullina has mentioned preventing inflation might be much less of a precedence and the central financial institution doesn’t anticipate to attain its 4% goal till 2024.

Post a Comment