In world’s first try to vary the path of an asteroid, scientists hope the strategy can forestall collisions with Earth.

A NASA spacecraft has hit an asteroid in an unprecedented take a look at designed to forestall doubtlessly devastating collisions with Earth.
NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Check (DART) spacecraft crashed into the asteroid Dimorphos about 11 million kilometres (6.8 million miles) from Earth at about 23:00 GMT on Monday.
The US house company livestreamed the take a look at from the mission operations centre exterior Washington, DC, exhibiting photographs taken by DART’s personal digicam because the cube-shaped “impactor” automobile, no larger than a merchandising machine with two rectangular photo voltaic arrays, careered into Dimorphos, an asteroid in regards to the measurement of a soccer stadium.
Cheers may very well be heard from engineers within the management room as second-by-second photographs of the goal asteroid grew bigger and in the end crammed the TV display screen of NASA’s stay webcast simply earlier than the spacecraft’s sign was misplaced, confirming it had crashed into Dimorphos.
“Impression confirmed for the world’s first planetary protection take a look at mission,” mentioned a graphic that appeared on the stay stream.
The mission was devised to find out whether or not a spacecraft can alter the trajectory of an asteroid via sheer kinetic power, nudging it off beam simply sufficient to maintain Earth out of hurt’s method.
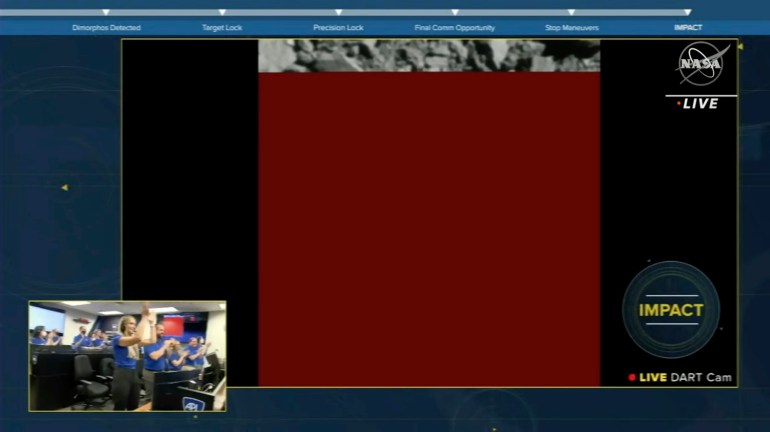
Its success is not going to be recognized till additional ground-based telescope observations are accomplished subsequent month.
“This can be a difficult take a look at, and because of this we’re taking these first steps now to develop this know-how earlier than we'd like it,” Nancy Chabot, the mission coordination lead, informed Al Jazeera hours earlier than the scheduled influence.
The DART spaceship launched from California in the US final November, and has made most of its journey with the steerage of NASA flight administrators.
There was a heightened sense of anticipation because the craft approached its goal.
“It’s the ultimate cosmic collision countdown,” tweeted mission management on the Johns Hopkins College Utilized Physics Laboratory within the US state of Maryland.
The asteroid didn't submit a danger to Earth, however the take a look at marks the primary effort to vary the trajectory of an asteroid utilizing solely kinetic power, and scientists hope that the strategy may very well be used to nudge asteroids and forestall cataclysmic collisions.
“If this works, then we all know we are able to use that very same know-how to deflect asteroids that may pose an precise risk additional down the road,” Tanya Harrison, a fellow on the Outer Area Institute in Seattle informed Al Jazeera.
A digicam despatched again photographs in the course of the remaining method and collision.
The goal was an asteroid “moonlet” that orbits an asteroid about 5 instances bigger, referred to as Didymos.
Smaller asteroids are extra widespread and subsequently a higher concern within the close to time period, making the Didymos pair appropriate take a look at topics for his or her measurement, based on NASA scientists and planetary defence specialists.
🛰️ That is solely a take a look at – of planetary protection. At this time, our #DARTMission is about to crash right into a non-hazardous asteroid to check deflection know-how, ought to we ever uncover a risk.
Impression: 7:14pm ET (23:14 UTC). Watch our LIVE broadcast at 6pm ET: https://t.co/VAfF5ZXcYBpic.twitter.com/czGqnYJIGJ
— NASA (@NASA) September 26, 2022
Their relative proximity to Earth and dual-asteroid configuration additionally make them sturdy topics for the primary proof-of-concept mission of DART.
The DART workforce hopes to shorten the orbital monitor of Dimorphos by 10 minutes however would think about a minimum of 73 seconds ample to show that the strategy may very well be used to deflect asteroids.
The price of the venture is estimated to be about $330m, far beneath a lot of NASA’s extra formidable house missions.
DART is the most recent of a number of NASA missions lately centered on exploring asteroids, rocky remnants from the photo voltaic system’s formation greater than 4.5 billion years in the past.

Post a Comment