5 years after crackdown by safety forces led to mass exodus from Myanmar, Rohingya stay caught in ‘merciless limbo’.
5 years in the past, a violent marketing campaign by safety forces in Myanmar sparked a mass exodus of about 730,000 Rohingya, who – carrying their belongings on their backs and typically crowding onto makeshift bamboo and jerry-can rafts – fled in the hunt for security. Most headed to neighbouring Bangladesh.
The violence – which included studies of gang rape, mass killings, and compelled expulsion – introduced renewed worldwide consideration to a long time of documented persecution in opposition to the principally Muslim Rohingya, who're largely stateless after years of what rights screens have known as systematic marginalisation by Myanmar’s authorities.
However as refugees, many Rohingya have discovered little reprieve as they mark the fifth anniversary on Thursday of what advocates name Rohingya Genocide Remembrance Day.
A United Nations report discovered that assaults on Rohingya have been carried out with “genocidal intent”, and in March, the USA turned the primary authorities to formally declare that the assaults constituted genocide. Myanmar has denied that any violence dedicated by safety forces amounted to genocide.
The group stays caught in a “merciless limbo”, in line with Norwegian Refugee Council chief Jan Egeland, as refugees deal with a backslide in rights and stagnating alternatives in Bangladesh, and grim prospects of a secure and dignified return to their house in Myanmar.
If Rohingya return to Myanmar, “there isn't any assure that the cycle of violence is not going to repeat once more,” Nay San Lwin, the co-founder of the Free Rohingya Coalition, informed Al Jazeera.
However in Bangladesh, he stated, “the refugees are feeling like they're the prisoners”.
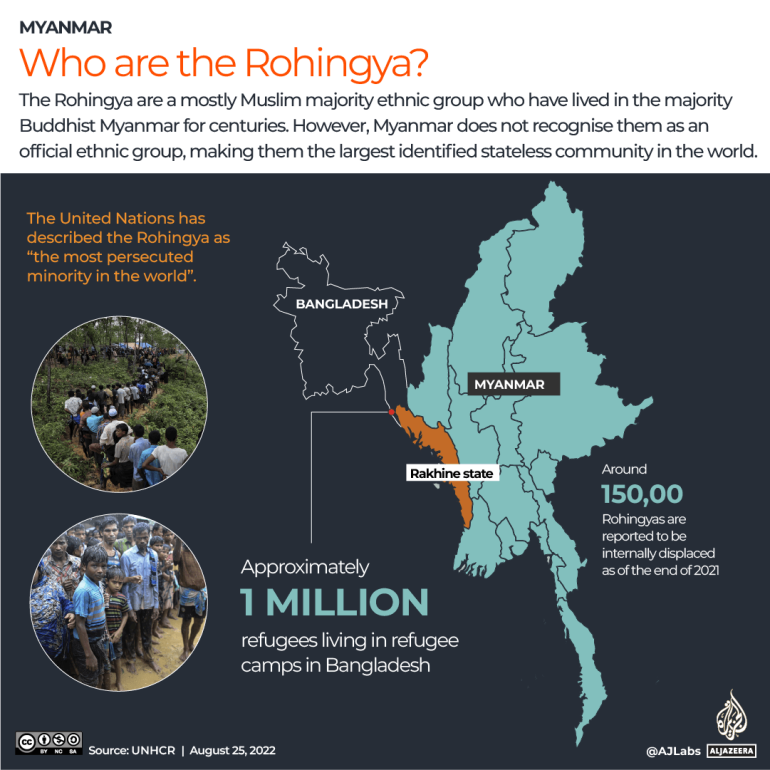
Who're the Rohingya?
The Rohingya are a predominantly Muslim ethnic group that hint their presence in modern-day Myanmar to the ninth century. They converse Rohingya or Ruaingga, a definite dialect, and preserve a novel tradition. They reside primarily in Myanmar’s Rakhine state alongside the nation’s western coast.
Greater than one million Rohingya have fled the nation amid a long time of presidency persecution, settling predominantly in Bangladesh, in addition to India, Pakistan and Malaysia, amongst different nations.
Whereas most Rohingya have been thought of equal residents underneath a regulation handed following Myanmar’s independence from British rule in 1948, the navy takeover of the federal government in 1962 led to the passage eight years later of the Emergency Registration Act, which restricted the rights of communities considered by the federal government as having international roots.
Documented persecution of the Rohingya escalated within the following years, because the military-led authorities sought to register all Rohingya, ensuing within the first main violent crackdown on the group in 1978. Throughout that interval, about 200,000 Rohingya fled to Bangladesh
In 1982, Myanmar’s authorities handed a citizenship regulation, which outlined full citizenship as primarily based on ethnicity; particularly, being a member of one of many 135 ethnic teams the federal government stated settled in Myanmar previous to the primary Anglo-Burmese struggle in 1824.
Myanmar’s management has usually maintained that a distinct Rohingya ethnicity doesn't exist, and that members of the Rohingya group are descendants from India and Bangladesh who migrated throughout Britain’s colonial rule from 1824 to 1948. That place has been challenged by historians.
“The narrative of the Rohingya has been overtaken by fiction, with their place in Myanmar’s historical past expunged by a succession of navy governments in search of scapegoats and aided by the nation’s already sturdy sense of Buddhist nationalism,” wrote Gregory Poling, the director of the Middle for Strategic Research’ Southeast Asia programme, in 2014.
Tensions between Rohingya and different Muslim and Buddhist communities have led to additional spates of state violence, most notably within the early Nineties, when about 250,000 Rohingya fled to Bangladesh, and between 2012 and 2014, when tens of 1000's extra left the nation.
In the meantime, rights teams have documented continuous strikes by Myanmar to render Rohingya residents stateless and marginalised, together with, in 2015, the federal government invalidating long-held identification playing cards and changing them with “nationwide verification playing cards” that require, amongst different stipulations, that Rohingya show three generations of residence in Myanmar and register as both “Bengali” or “Muslim”, however not Rohingya.
In Myanmar, rights screens proceed to document restrictions on Rohingya, which have included limits on motion, schooling, employment and childbearing. About 600,000 Rohingya at the moment stay in Myanmar, with greater than 130,000 dwelling in restrictive inner displacement camps contained in the nation.
The violence that preceded the most important Rohingya exodus in historical past started in October of 2016, following an assault claimed by a Rohingya-linked group on border police posts in Rakhine state. Myanmar stated 9 personnel have been killed within the assaults.
In response, the federal government launched what Amnesty Worldwide known as a “scorched-earth marketing campaign” that included illegal killings, a number of rapes and the burning of complete villages.
Tens of 1000's of Rohingya fled to Bangladesh through the months-long crackdown, with a United Nations official saying Yangon was committing “ethnic cleaning”, outlined by the UN as utilizing drive or intimidation to render an space ethnically homogenous.
The following wave of violence started on August 25, 2017, when Myanmar stated 10 cops had been killed in a sequence of coordinated assaults in a single day claimed by the Arakan Rohingya Salvation Military (ARSA). The insurgent group has stated the assaults have been in response to abuses dedicated in opposition to Rohingya.
The ensuing authorities crackdown, known as a “clearance operation”, noticed tons of of Rohingya villages fully razed, Rohingya civilians murdered en masse, and ladies subjected to gang rape, in line with a UN fact-finding mission report revealed a 12 months later.
The report stated the assaults have been carried out with “genocidal intent” and that the nation’s commander-in-chief and 5 generals needs to be prosecuted.
Greater than 700,000 Rohingya fled Myanmar within the following days, with some moms recounting tales of infants ripped from their arms and thrown into fires by troops or nationalist teams. Witnesses and rights screens additionally reported that Myanmar troops fired on these making an attempt to flee to the border with Bangladesh.
In southeastern Bangladesh, in simply weeks, an array of refugee camps swelled from about 300,000 Rohingya residents to about a million, swiftly changing into the world’s largest refugee settlement.
The inflow added important stress to Bangladesh, the place a couple of quarter of the inhabitants was already dwelling in poverty, in line with the World Financial institution. Inflation and value of dwelling costs have additionally soared throughout the nation following the Russian invasion of Ukraine on February 24, placing additional stress on Bangladesh’s inhabitants of about 165 million.
The prospect of a return to Myanmar has been made extra sophisticated by the November 2021 navy takeover of the nation, which has successfully ended the nation’s decade-long transition to partial civilian rule, though some analysts have argued the navy repression could also be softening most people’s place in direction of Rohingya.
In line with Disaster Group’s Myanmar and Bangladesh analyst Thomas Kean, practically the entire roughly 730,000 Rohingya refugees who fled to Bangladesh within the second half of 2017 stay within the refugee camps there, though there have been a number of situations of refugees making an attempt perilous sea journeys in hopes of discovering a greater state of affairs.
Thus far, not a single refugee in Bangladesh has opted to return to Myanmar underneath a proper, and controversial, repatriation deal reached between the 2 nations in November 2017, simply three months after the crackdown started, in line with Kean. Subsequent makes an attempt to persuade the refugees to return in 2018 and 2019, additionally failed.
Whereas Bangladesh has largely honoured the idea of non-refoulement, which prohibits the forcible return of refugees, Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina informed the UN human rights chief on August 17, 2022, that the “Rohingya are nationals of Myanmar and so they should be taken again”.
UN Excessive Commissioner for Human Rights Michelle Bachelet informed reporters on the time that circumstances in Myanmar have been “not proper for returns”.
The federal government of Bangladesh has sought cooperation from China to maneuver ahead with repatriation efforts.
Bangladesh has additionally moved forward with the controversial plan to maneuver 1000's of Rohingya refugees to the remoted and flood-prone Bhasan Char island.
In the meantime, rights teams and residents have reported a rise in restrictions for Rohingya within the camps that severely “restrict livelihoods, motion, and schooling”, in accordance to Human Rights Watch.
Restrictions have included the destruction of 1000's of retailers within the camps in Bangladesh, the place Rohingya refugees can't legally work, and the closure of some non-public colleges, the one type of schooling obtainable past aid-agency offered main education.
They've additionally included the development of fences round camps and permission necessities to journey exterior of 1’s house camp.
“We can't transfer freely,” Khin Maung, govt director of Rohingya Youth Affiliation (RYA) and resident of the Kutupalong refugee camp, informed Al Jazeera. “We're doing our greatest, however we can't perform our exercise conveniently. We've no proper to do our work freely, so we aren't free in any respect.”
In the meantime, residents have reported feeling more and more caught between a spike in crime dedicated by gangs jockeying for management of the camps, and the ensuing crackdown by police.
A sequence of arrests adopted the killing of human rights activist and Rohingya chief Mohibullah within the Kutupalong refugee camp in September of 2021. Bangladesh blamed the killing on the ARSA.
For the Rohingya, something approaching justice stays a far-off hope, though a number of worldwide investigations are at the moment probing allegations of genocide dedicated by Myanmar.
Essentially the most outstanding case has been one introduced by The Gambia, a small West African nation on the United Nations’ high court docket, the Worldwide Court docket of Justice, which alleges Myanmar dedicated genocidal acts “meant to destroy the Rohingya group in entire or partly”.
The case has already seen then-Myanmar State Counsellor Aung San Suu Kyi testify in defence of the navy in 2019, saying any perpetrators can be prosecuted pending an inner investigation, whereas denying doable crimes dedicated by safety forces amounted to genocidal intent.
The Myanmar authorities’s investigation later stated that some safety forces deliberately killed or displaced civilians, amounting to “doable struggle crimes”, however stated there was no proof to help the genocide claims. Aung San Suu Kyi was deposed through the 2021 coup and is at the moment underneath home arrest.
Judges within the ICJ case have already adopted provisional measures that require Myanmar to stop all genocidal acts in opposition to the Rohingya and to protect proof associated to the case, whereas rejecting Myanmar’s opposition that The Gambia didn't have standing to deliver the case.
The ICJ case is just not felony, however a discovering in The Gambia’s favour may “present the impetus for higher worldwide motion in direction of justice for all victims of the Myanmar safety forces’ crimes”, in line with Elaine Pearson, the performing Asia director at Human Rights Watch.
The Worldwide Legal Court docket (ICC) in 2019 additionally accredited opening an investigation into the crackdown, arguing that it falls underneath ICC jurisdiction as a result of, not like Myanmar, Bangladesh is a signatory to the Rome Statute, which created the court docket.
In contrast to the ICJ, the ICC can attempt particular person perpetrators for worldwide crimes. In February 2022, ICC prosecutor Karim Khan made his first investigative go to to Bangladesh.
The probe might be aided by a tranche of paperwork obtained by a non-profit struggle crimes investigative organisation, which appeared to point out a coordinated plan by Myanmar navy officers to assault and expel Rohingya and conceal it from the world, as reported by Reuters information company in early August.
Argentina’s justice system has additionally opened a struggle crimes investigation into the Rohingya, following a lawsuit filed by the UK-based Burmese Rohingya Organisation (BROUK). The choice falls underneath the authorized idea of “common jurisdiction”, which states that some crimes are so extreme their prosecution is just not confined to a single jurisdiction.
In March, the USA turned the primary authorities to declare the assaults on Rohingya represent genocide, a largely symbolic transfer that might rally allies to take related measures.
What occurred through the 2017 authorities crackdown and mass exodus?
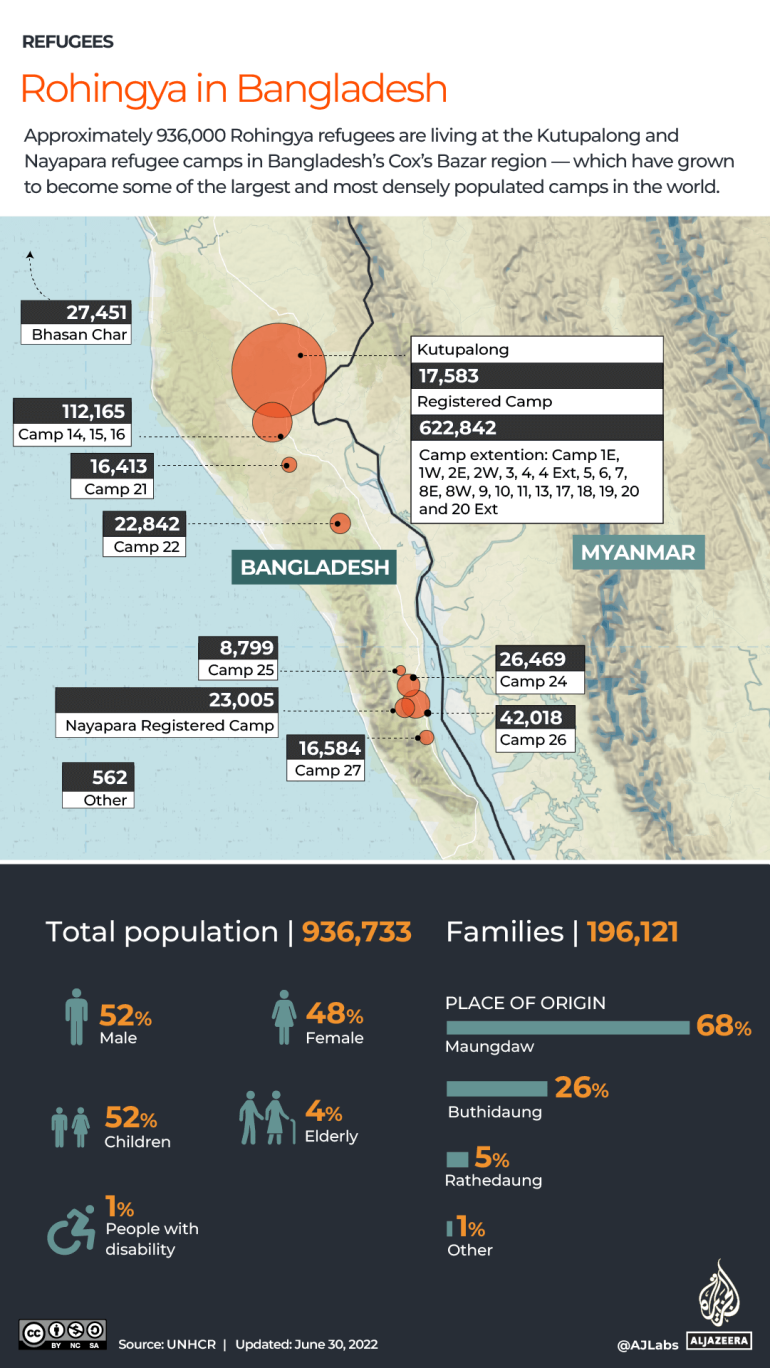
What has occurred in Bangladesh?


Post a Comment